How the Pan-African Payment and Settlement System (PAPSS) works – Chimaobi Agwu
PAPSS – the Pan-African Payment and Settlement System – is an African cross-border, financial market infrastructure that enables payment transactions across African countries in a secure and timely manner. The platform reduces risk and helps with regional financial integration. PAPSS is a facility created by the African Union in partnership with the African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank) to support trade under the African Continental free Trade Area (AfCFTA). PAPSS supports payment agreements that will increase the amount of trade between African nations and will also make it easier for central banks to integrate their economies and finances.
PAPSS provides a payment and settlement service to which commercial banks, payment service providers, and fintech organizations across the continent can connect as participants in conjunction with central banks in the continent.
There are currently 42 different currencies used in Africa. The PAPSS enables businesses in Africa to settle commercial transactions inside the continent using their home currency. PAPSS is anticipated to lower expenses and hasten trade transaction settlement and payment.
Traditionally, to settle payments between two African currencies in a third, external currency, typically dollars or euros, African businesses and their local banks relied on correspondent banks, frequently located outside of Africa. Individual African Central Banks had to meet foreign exchange and liquidity criteria under the prior arrangement. PAPSS, which is widely regarded as a game-changer for intra-African trade, aims to reduce transaction costs for firms on the continent by USD 5 billion annually.
Via a straightforward, inexpensive risk-controlled payment clearing and settlement mechanism, the platform offers an alternative to the present expensive and time-consuming correspondent banking relationships, facilitating trade and other economic activity among African countries. Also, it provides a way to monitor funds transfers and broaden financial inclusion to include the unorganized sector, thereby lowering money laundering, which costs the continent several billions of dollars every year.
The real-time infrastructure of PAPSS offers a dependable, affordable solution for quick payments, whether it be for online shopping, money transfers, salary payments, trading stocks and shares, or high-value commercial transactions.
The PAPSS network will have 8 central banks, 28 commercial banks, and 6 switches as of June 2022. Before the end of 2023, it will reach all five of Africa’s regions. By the end of 2024, all central banks must register, and by the end of 2025, all commercial banks must do the same.
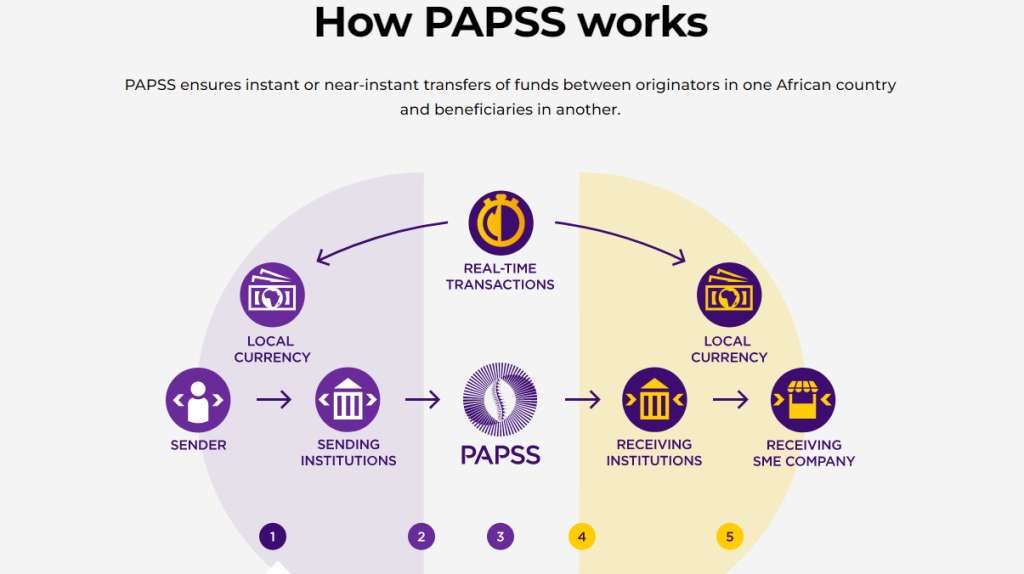
HOW DOES PAPSS WORK?
Afreximbank claims that PAPSS operates through three main procedures:
- PAYMENTS INSTANT FOR HOMES AND BUSINESSES: Any African nation’s citizens and businesses are welcome to visit an authorized participant (commercial bank). The PAPSS then verifies the payment instructions received by the bank before the bank sends money to them. PAPSS transmits verified payment instructions to the beneficiary bank. Payment is made to the receiver in that country’s currency.
- PRE-FUNDING BY DIRECT PARTICIPANTS: On the basis of pre-funding agreements from participants, this procedure is intended to assure secure transfers for both sides (sender and receiver). after the direct participant has communicated payment instructions to PAPSS. In the pre-funding process, Direct Participants integrate directly with PAPSS and the real-time gross settlement (RTGS) systems of central banks. Direct Participants who have the necessary liquidity can help Indirect Participants (participants without settlement accounts) fund or defund their clearing accounts on PAPSS. The ISO 20022 communications standard is used to provide notifications, informing PAPSS, the Participants, and RTGS of the progress of each step of the transaction.
- SETTLEMENTS TO SIMPLIFY TRANSACTIONS IN LOCAL CURRENCY: Important organizations including Afreximbank, PAPSS, and central banks are involved in the settlement. How? All participating central banks’ net positions in local currency are calculated by PAPSS. Depending on the net position, the payment platform transmits credit or debit settlement instructions to the real-time gross settlement system (RTGS) of the central bank. Between the PAPSS pre-funded account and the Central Bank suspense account, the Central Bank RTGS debits or credits and confirms settlement to PAPSS. To complete local currency settlement, PAPSS reflects instructions from the central bank. Afreximbank receives comparable hard currency settlement instructions from PAPSS based on the net position. The central banks’ hard currency settlement accounts held by Afreximbank are credited or debited, and Afreximbank confirms this to PAPSS. Transactions are performed and monitored by participants in a maximum of 24 hours.
The following actions must be followed in order to send payments via the PAPSS: Payment instructions are issued by a business to their local bank or payment service provider; the bank then sends the instructions to their Central Bank, which then sends them to PAPSS; PAPSS validates the instruction and forwards it to the beneficiary’s Central Bank and local bank; and finally, the local bank pays the beneficiary the transferred funds in local currency.
PAPSS works by linking the individual African Central Banks’ real-time gross settlement (RTGS) systems. Every day, PAPSS nets out the balance of all transactions between different African currencies, settling the amount before midnight. The remaining discrepancy is then resolved by central banks. The following day, the payment and settlement procedure begins anew at net zero.
- The bank or payment service provider receives a payment instruction from the originator in their home currency.
- The PAPSS receives the payment instruction.
- PAPSS performs all required payment instruction validation checks.
- The beneficiary’s bank or payment service provider receives the payment instruction.
- The money are transferred to the beneficiary through their local currency clearing at their bank.
How PAPSS settlements are made
Within 24 hours, PAPSS must assure fast payment. Every day at 11.00 UTC, net settlement between all participating central banks takes place.
- PAPSS calculates the net position in local currency for each participating central bank at End of Day (currently 11 a.m. UTC).
- PAPSS delivers instructions to the Central Bank RTGS for credit or debit settlement (depending on net position).
- Between the PAPSS Pre-funded Account and the Central Bank Suspense Account, the Central Bank RTGS debits or credits and confirms payment to PAPSS.
- To complete local currency settlement, PAPSS reflects instructions from the central bank.
- Afreximbank receives comparable hard currency settlement instructions from PAPSS based on the net position.
- Afreximbank verifies to PAPSS and credits or debits the central bank’s hard currency settlement account.
PAPSS services
PAPSS Core service
The PAPSS Instant Payment System (PIPTM), which facilitates both wholesale and retail real-time payments as well as the networking of banks and payment service providers, provides the main service for PAPSS.
Major PAPSS Quick Payment Features
- Instantaneous, unconditional credits to customer accounts
- immediate confirmation to the recipient and the originator
- Services are offered 365 days a year, nonstop
- Interoperability, big data sets, and rich data for payment and remittance information are all possible using the ISO 20022 global messaging standard.
- a safe infrastructure with technologies for preventing payment fraud and cybercrime, supported by behavioural analytics and machine learning.
PAPSS Overlay services
Participants may use additional and optional services aimed at various customers to provide services to their clients.
- Request to Pay (R2P) enables flexible real-time billing, invoicing, and money collection for banks and other financial institutions’ clients (big corporations, cooperative societies, service providers, etc.) who use cross-border direct debit payments. When payments are due, a central system for managing cross-border debit transfer mandates will collect the collected debits and transmit them on to the instant credit system for clearing and settlement.
- Escrow service: A safe and secure agreement for commercial and other banks that places the cash necessary to complete a transaction in PAPSS’s custody until the transaction is finished, increasing the protection of buyers and sellers who are trading while also controlling payments.
- Remittance service: When permitted by law, low-cost intra-African remittance services with quick beneficiary access to the funds via a bank account, a digital wallet, or cash out.
- Proxy addressing is a service that makes it possible to send and receive payments via PAPSS using aliases such an email address, national ID, phone number, etc.
- Sanctions Screening – A service that checks transactions against databases like the UN Sanctions List, OFAC, etc. is known as sanctions screening.
The Central Banks are establishing connections with the top local banks during the initial phase of PAPSS implementation. According to reports, PAPSS has already established connections with 25 of the continent’s biggest commercial banks, including institutions like Ecobank, Zenith Bank, and Standard Bank (aka Stanbic). Licensed local fintech businesses may have access to PAPSS in a later stage of its development, enabling them to handle trade-related transactions for intra-African trade, especially on mobile platforms. The Ghana Interbank Payment and Settlement Systems Ltd platform would allow banks and non-bank financial institutions in Ghana, such as savings and loan organizations, fintechs, and mobile money platforms, to use PAPSS.
Moreover, PAPSS and BUNA, the Arab Monetary Fund’s cross-border, multi-currency payment system, have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) (AMF). By the MOU, BUNA and PAPSS will eventually be able to communicate with one another.
Benefits of PAPSS – Pan-African payment settlement system
- Inexpensive – Reduction of fees for correspondent banking and delays at the central office.
- Simple – Compared to the present fragmented client’s FX buy approach, it enables clients to fully fund their trade obligations.
- Quick – Payment made right away in local currencies.
- Seamless – Eliminates reliance on foreign currencies and correspondent banks; makes intra-African trade easier.
PAPSS advantages for participants
Benefits of PAPSS include facilitating cross-border payments for clients for financial intermediaries, commercial banks, fintech firms, and payment service providers (PSPs) – Direct Participants and Indirect Participants. They can anticipate the following:
A platform for creativity and innovation plus wider market access APIs that improve scale, performance, security, and privacy
client service that is quicker and more effective
Performance of cross-border payments is now more straightforward and doesn’t need as many correspondent banking partnerships.
Analytical data from ISO 20022 standard messaging for management reporting to aid in making wise decisions
PAPSS advantages for African Governments
Connecting with PAPSS has numerous advantages for governments and central banks as well:
- Reduced foreign exchange demand plus reduced current account pressure
- More supervision of international transactions due to increased openness enhances the possibility of income generation.
- Financial inclusion was expanded, and economic growth was enhanced.
Benefits of PAPSS to customers
The following are advantages for both big and small businesses, as well as for people whose payments and remittances are processed through PAPSS:
- Payments across African borders almost instantly without currency conversion
- Increased working capital due to speedier transactions and assured payments
- For millions of Africans, especially those who were previously underserved, access to payment-facilitating choices
How to Get PAPSS as a household or as a business owner
- Visit an authorized participating commercial bank in your country.
- Fill out the PAPSS application and submit it with a visible trade transaction.
- Eligible transactions are those that fall within PAPSS Memorandum (In Nigeria it is Memorandums 9 and 10 of the CBN FX manual), such as export transactions and import Letters of Credit.
- Importing products must be with an African origin
- The beneficiary must be in one of the countries that make up the West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ), including Nigeria, Gambia, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ghana, and Guinea of a PAPSS participating country
- Beneficiary Bank must participate in PAPPS, and the instructions must include a Form M/NXP reference for the transaction and remittance information.
- Payment is forwarded from the bank to PAPSS, which verifies the supplied payment instructions.
- PAPSS transmits verified payment instructions to the beneficiary bank.
- Payment is made to the receiver in that country’s currency.
How to get PAPSS Using the PRE-FUNDING OPTION
To ensure secure transfers for both parties, this procedure is used (sender and receiver). Participants must, however, agree to the pre-funding agreement.
- After the direct participant has communicated payment instructions to PAPSS.
- In the pre-funding process, direct participants integrate directly with PAPSS and the real-time gross settlement (RTGS) systems of central banks.
- Indirect Participants (those without settlement accounts) who do not have RTGS accounts can fund or defund their clearing accounts on PAPSS with the help of a direct participant who is able to provide the necessary liquidity.
- The ISO 20022 messaging standard is used to transmit notifications, informing PAPSS, the participants, and RTGS of the progress of each step of the transaction.
PAPSS Transaction process
- The client visits the branch and requests a PAPSS application.
- The application form is given due consideration.
- The Bank authorizer verifies for completeness and correctness CBN permission is acquired for the transaction.
- Principal and associated fees are debited from the client’s local currency account in his home country.
- The recipient is compensated in their country’s currency.
- The customer gets informed.
- Settlement is done using local money.
What you get from PAPSS – Pan-African payment and settlement system
- Instant payment in local currencies.
- Guarantees the final settlement of the funds to the recipient participant.
- The beneficiary has immediate availability of funds.
- Removes the dependencies on third currencies and correspondent banking; facilitates intra-African trade.
- Drive the Africa Continental Free Trade Area agreement (AfCFTA) to yield growth in transactional activities (trade and payments) from corporates and retail clients.
- Reduction in costs associated with correspondent banking fees and central delays.

Different Participants in PAPSS – Direct and indirect participants
To carry out pre-funding, Direct Participants keep a settlement account with the central bank of the nation in which they conduct business..
Direct Participants are banks and other financial institutions that
- have a settlement account with the central bank of the country in which they operate and
- comply with all financial and regulatory competency requirements of that central bank.
Direct Participants will then need to meet further qualifying requirements.
In the nation of operation, Indirect Participants don’t keep a settlement account. Instead, they work with a direct participant because they require the liquidity of the direct participant to fund or defund clearing accounts. Furthermore, indirect participants includes Banks and other financial institutions that do not have a settlement account with the central bank of the nation in which they conduct business may also be considered indirect participants. To help with the settlement of payment instructions, they will be allowed to enter into individual sponsorship agreements with Direct Participants. Then, indirect Participants will need to fulfill additional eligibility criteria.
WHAT IS THE EXCHANGE RATE FOR TRANSACTIONS UNDER PAPSS
For cross-border payments made through the Pan-African Payment and Settlement System, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) ordered commercial banks to adopt the exchange rate in the importer and exporter window (I&E) in October 2021. (PAPSS).




