Growth in broadband penetration in Nigeria – Coronation Merchant Bank
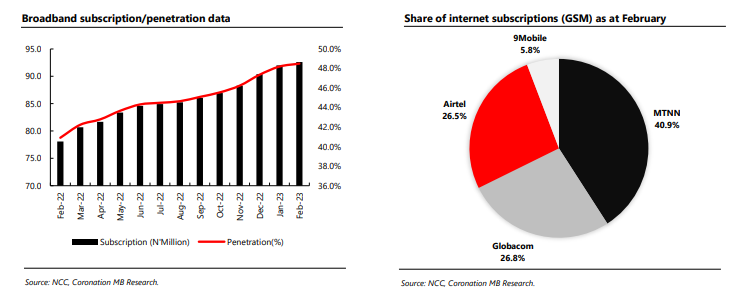
According to the most recent data given by the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC), the industry regulator, internet subscribers were N156.9 million in February.
’23, reflecting a 0.5% m/m increase (or around 743,000 new memberships). Meanwhile, internet subscriptions climbed by 10% year on year. The rise can be ascribed in part to growing use of digital services. However, we recognize that increases in headline inflation have weighed on internet subscription activity, reducing consumer expenditure.
In February ’23, MTNN had the highest percentage of internet subscriptions (40.9%). Globacom, Airtel, and 9Mobile accounted for 26.8%, 26.6%, and 5.8% of the market, respectively. MTNN, Globacom, and 9Mobile all experienced m/m growth in internet subscriptions of 0.9%, 0.8%, and 0.7%, respectively. Meanwhile, Airtel experienced a -0.5% decline (the company’s second decline this year).
According to MTNN’s FY2022 figures, service income climbed by 21.6% year on year. The increase can be ascribed in part to strong growth in data income (47.9% year on year), which was sparked by a year on year increase in active data subscriptions as a result of the launch of 5G spectrum in seven locations across Nigeria’s six geopolitical regions.
Despite Nigeria’s high inflation, currency volatility, and global economic shocks that disrupted supply chains, the telecoms industry has remained robust. According to the NBS’s most recent national accounts, the sector increased by 10.7% year on year in FY2022 and contributed approximately 13.6% to GDP. According to a second NBS study, capital importation in the telecoms sector increased 117% year on year to USD168.3 million in Q4 ’22, indicating the sector’s capacity to attract foreign investments despite a foggy macroeconomic environment.
According to the most recent inflation statistics, the communications sector climbed by 10.5% year on year in March ’23, compared to 10.3% year on year the previous month. This can be ascribed in part to increases in operating expenses.
The proposed 5% excise levy on telecoms services, first mentioned in the 2020 Finance Act, was included in the newly disclosed fiscal measures for 2023. This excise levy, however, was not implemented. We notice that a circular issued by the federal ministry of communications indicates a greater willingness to enact this 5% telecoms excise levy. It is scheduled to go into effect in June of 23. We believe that mobile network operators, who are already dealing with inflationary pressures, will pass the financial burden onto users.
Given the present penetration level of 48.5% (February ’23), the FGN’s broadband penetration objective of 90% by 2025 is ambitious.
The advantages of increased broadband penetration are numerous. They include increasing the country’s social capital, which is strongly linked to major increases in education and local entrepreneurship, as well as potential reductions in the high unemployment rate.
Regarding the 5G spectrum, we learn that MTNN has pushed out approximately 588 5G sites throughout major cities in Nigeria. It is also worth noting that the corporation expects to attain 10% 5G network penetration by the end of 2023. Regarding Airtel, who was the single bidder in another (and most recent) 5G auction held in December ’22, there have been no public updates on roll out efforts.
Despite the hazy macroeconomic environment, opportunities for further growth remain high, particularly in the areas of broadband expansion and deployment across the country, as demand for digital services, given the growing need for financial inclusion, and smartphone adoption across the country continues to improve.




